Shoulder Pain
Conditions
What is Shoulder Pain?
As you age, you’re more likely to experience shoulder pain from a variety of common conditions. The pain can come on gradually or abruptly, and it may range from mild to excruciating. Shoulder pain may arise from the shoulder joint itself or from any of the many surrounding muscles, ligaments, or tendons.
What causes shoulder pain?
Several factors and conditions can contribute to shoulder pain. The most prevalent cause is rotator cuff tendinitis.
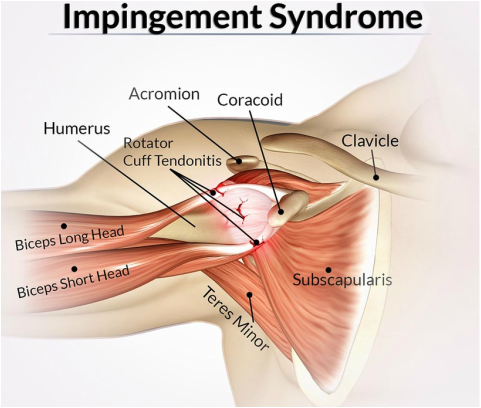
This is a condition characterized by swollen tendons. Another common cause of shoulder pain is impingement syndrome where the rotator cuff gets caught between the acromium (part of the scapula that covers the ball) and humeral head (the ball portion of the humerus).
Sometimes shoulder pain is the result of injury to another location in your body, usually the neck or biceps. This is known as referred pain. Referred pain generally doesn’t get worse when you move your shoulder.
Other causes of shoulder pain include:
- Arthritis
- Torn cartilage
- Torn rotator cuff
- Swollen bursa sacs or tendons
- Bone spurs (bony projections that develop along the edges of bones)
- Pinched nerve in the neck or shoulder
- Broken shoulder or arm bone
- Frozen shoulder
- Dislocated shoulder
- Injury due to overuse or repetitive use
- Spinal cord injury
- Heart attack
How can shoulder pain be treated?
Treatments will vary, depending upon what exactly is causing your shouder pain.
Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) injection contains a concentration of many different growth factors that appear to reduce inflammation and promote healing. These types of injections tend to work better in people whose shoulder pain is caused by tendon tears, tendinitis, or injury.
Stem Cell Therapy for shoulder pain is minimally invasive. It’s a procedure that can decrease inflammation, slow and repair all these forms of damage from arthritis, and delay or prevent surgery.
Microcurrent Therapy helps injured tissue heal faster and provides relief from pain caused by injury or chronic conditions. Your body has a natural electrical current that provides intercellular communication through electromagnetic signaling. When you have an injury, this signaling is disrupted or diminished. Without the proper electromagnetic signals, your cells cannot do their job efficiently.